Introduction
3D printing technology is transforming industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to fashion and automotive. As businesses and individuals explore its potential, many questions arise about how it works, where it’s heading, and real-world applications. This blog post will address common questions, discuss key industry trends, and highlight case studies showcasing the power of 3D printing.
1. Common Questions About 3D Printing
What is 3D Printing?
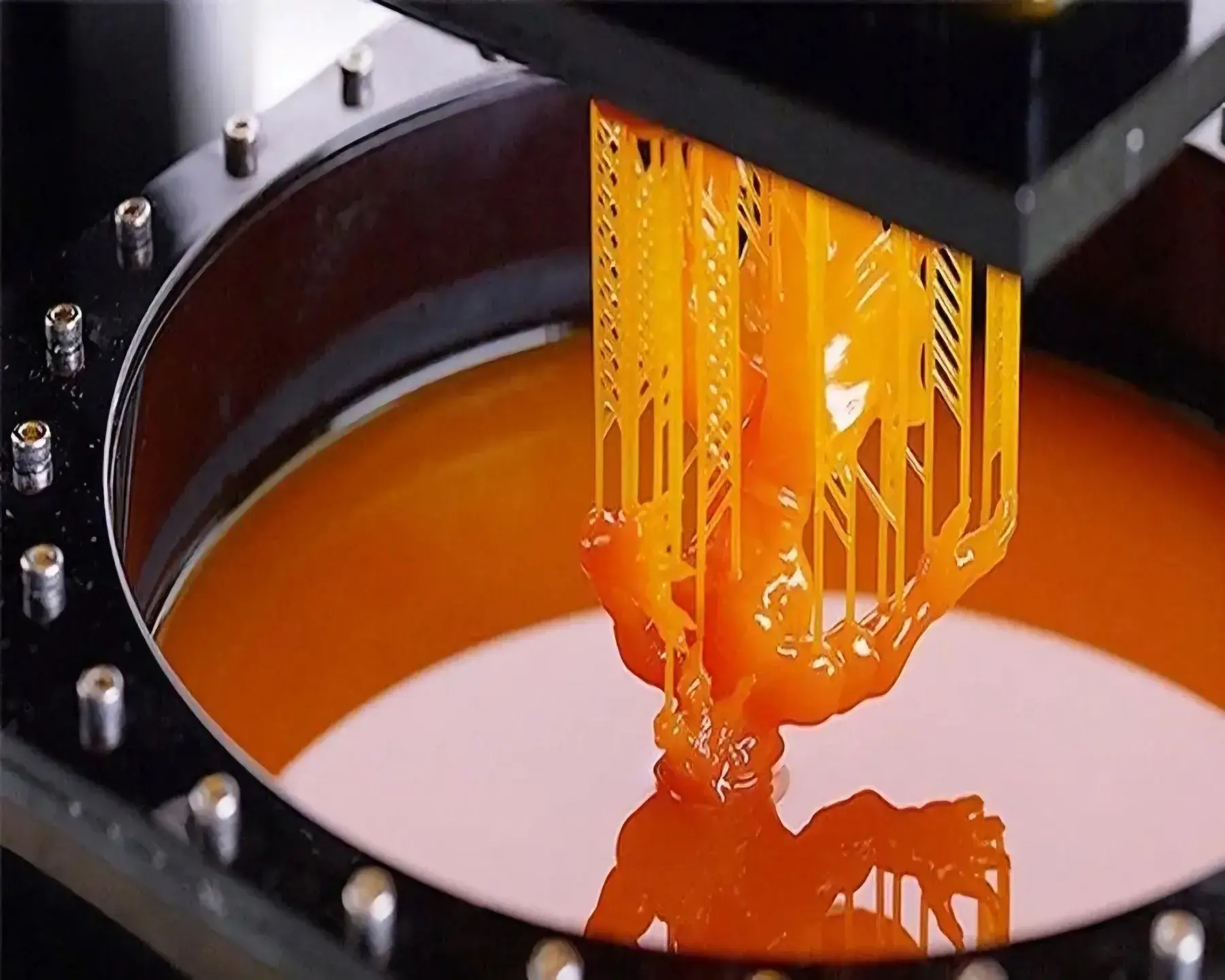
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer using digital designs. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, which involves cutting away material from a solid block, 3D printing builds objects from the ground up using various materials such as plastic, metal, resin, and even bio-materials.
What Are the Different Types of 3D Printing Technologies?
There are several 3D printing techniques, but the most commonly used include:
•Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Uses thermoplastic filaments melted and layered to create objects.
•Stereolithography (SLA): Uses UV light to cure liquid resin into solid structures.
•Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Utilizes a laser to fuse powdered material (often nylon) into solid objects.
•Metal 3D Printing (DMLS/SLM): Uses high-powered lasers to fuse metal powders for industrial applications.
What Are the Benefits of 3D Printing?
•Customization: Enables the creation of highly customized products, from prosthetic limbs to intricate jewelry designs.
•Speed and Efficiency: Rapid prototyping allows businesses to test designs quickly before full-scale production.
•Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces material waste and eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling.
•Sustainability: Some 3D printing technologies use recycled materials, reducing environmental impact.
2. Industry Trends in 3D Printing
a) Growth of Industrial 3D Printing
While 3D printing started as a prototyping tool, it is now used for full-scale manufacturing in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. Companies like Boeing and Tesla are integrating 3D-printed components into their production processes.
b) Advancements in 3D Printing Materials
New materials, including carbon fiber composites, biodegradable filaments, and bioprinting materials, are expanding the possibilities of 3D printing. These innovations improve strength, durability, and environmental sustainability.
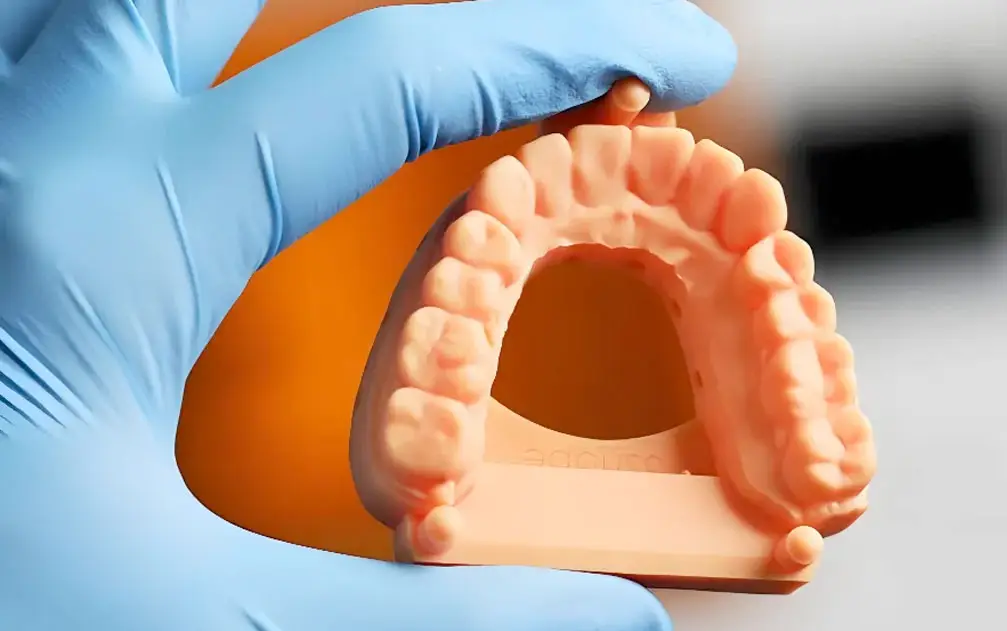
c) 3D Printing in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is benefiting from 3D printing through:
•Patient-Specific Implants: Custom-made orthopedic and dental implants.
•Bioprinting: Research into printing human tissues and organs for transplantation.
•Medical Equipment: Low-cost, customized prosthetics and surgical tools.
d) Sustainability and Eco-Friendly 3D Printing
With growing environmental concerns, many 3D printing companies are focusing on:
•Using recycled and biodegradable materials.
•Developing zero-waste manufacturing processes.
•Implementing circular economy principles, where old 3D-printed items are recycled into new products.
e) 3D Printing in Construction
3D-printed homes and infrastructure are gaining traction as companies develop faster, cheaper, and more sustainable building methods. The first 3D-printed communities are being developed in areas facing housing shortages.
3. Case Studies: Real-World Applications of 3D Printing
Case Study 1: 3D Printing in Aerospace
Company: Airbus
Airbus has integrated 3D printing into its aircraft production process, using it to create lightweight components that reduce overall weight and improve fuel efficiency. The company has successfully produced titanium 3D-printed brackets used in A350 aircraft.
Case Study 2: 3D Printing in Healthcare
Organization: The University of Michigan
Surgeons at the University of Michigan successfully used 3D printing to create a customized airway splint for a baby with life-threatening breathing issues. The device was bioresorbable, meaning it would dissolve in the body over time.
Case Study 3: 3D Printing in Fashion
Brand: Adidas
Adidas has launched its Futurecraft 4D sneakers, which feature 3D-printed midsoles designed for optimal comfort and performance. This move highlights the role of 3D printing in mass customization and sustainable manufacturing in the fashion industry.
Conclusion
3D printing is no longer just an emerging technology—it’s a game-changer across multiple industries. From healthcare to aerospace and fashion, businesses are leveraging its capabilities to create innovative, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions. As materials and technologies continue to advance, the future of 3D printing looks more promising than ever.